Category: mobile
-
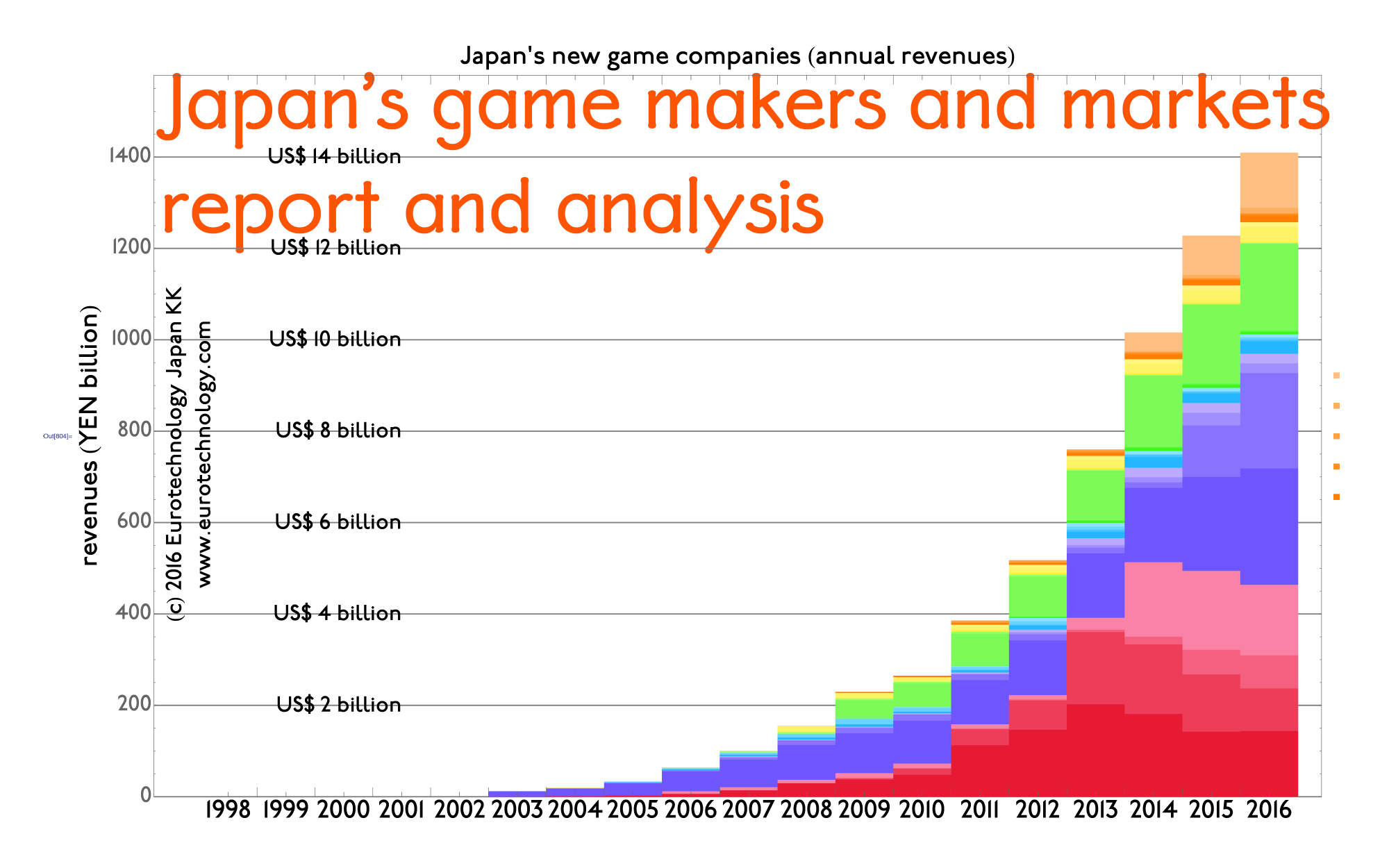
Google Play apps Japan: which android apps show highest revenues?
Top grossing apps (Feb. 18, 2015) Google play apps Japan ranking in Japan by gross revenues AppAnnie showed that in terms of combined iOS AppStore + Google play apps Japan revenues, Japan is No. 1 globally, spending more than the USA. Therefore Japan is naturally the No. 1 target globally for many mobile game companies!…
-

Japan apps: which are the top grossing apps in Japan’s iPhone app store?
Top grossing app ranking (Feb. 10, 2015) by Gerhard Fasol AppAnnie showed that in terms of combined iOS AppStore + Google Play revenues, Japan is No. 1 globally, spending more than the USA. Therefore Japan is naturally the No. 1 target globally for many mobile game companies, and quite a few of the top grossing…
-

Vodafone Japan could have been a business worth US$ 50 billion today! Why did Vodafone Japan fail and sell to SoftBank?
What can we learn from Vodafone’s failure in Japan? by Gerhard Fasol Had Vodafone been successful in Japan, Vodafone’s Japan business could be worth € 40 billion (US$ 50 billion) today In a separate blog post “EU-Japan Management: What is the value of good management?” we analyze what the value of Vodafone’s Japan business might…
-
NOKIA (handsets) quits Japan – for now… networks stay and grow
NOKIA’s Japan subsidiary was founded on April 3, 1989 – almost 20 years ago. On November 27, 2008 NOKIA announced to terminate selling mobile phones to Japan’s mobile operators, effectively withdrawing from Japan (except for purchasing, R&D and VERTU). NOKIA’s sales figures in Japan were a well kept secret until last week when several Japanese…
-
Help – my mobile phone does not work! – Why Japan’s mobile phone sector is so different from Europe’s
Presentation at the Lunch meeting of the Finnish Chamber of Commerce in Japan (FCCJ) on March 16, 2007 at the Westin Hotel, Tokyo. Find the summary and photos of the meeting here Download the presentation here From the Announcement: In his presentation, Dr. Fasol will explain the essentials of Japan’s mobile phone market, why and…